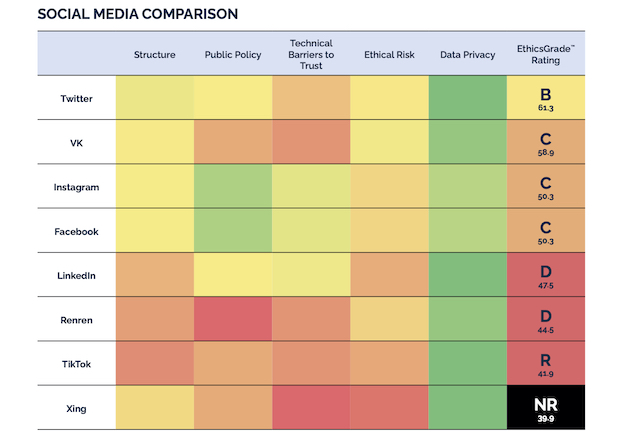
Cendana has raised a $30 million ‘fund of funds’ for VCs managing $15 million or less
Cendana Capital, a San Francisco-based fund of funds manager, has amassed stakes in more than 100 venture firms since launching in 2010. For the most part, it did this by focusing on managers who are raising funds of $100 million or less in capital, even foregoing stakes in beloved outfits like Forerunner Ventures and Uncork Capital as their assets under management ballooned well beyond that amount.
Yet as the market changed, however, Cendana founder Michael Kim began to play with that formula. Last spring, for example, when he closed on $278 million in new capital commitments, he said planned to invest in the mostly the seed-stage managers he has always backed, but that he planned to funnel a small amount of capital to pre-seed managers raising $50 million or less, as well as to invest in a sprinkling of international managers.
Now Kim is back with a new idea, and a new fund, that sees him covering even more ground. Called Cendana’s Nano fund, it has raised $30 million in capital from existing Cendana backers to invest in up to 12 investment managers who are piecing together funds of $15 million or less capital. There are simply too many smart people right now making smaller bets for Cendana not to make the move, he suggests. We talked with Kim about the fund — and the changing landscape more broadly — late last week. Our chat has been edited lightly for length.
TC: What’s the thesis behind this Nano fund?
MK: The seed market has evolved a lot over the last 18 months to 24 months. You have this whole world of Twitter VC, meaning people who have a lot of strong opinions and an operator-investor perspective, but who may not have substantial funds behind them. You have solo capitalists like Lachy Groom and Josh Buckley, who’ve gone out and raised hundreds of millions of dollars. You also have the AngelList rolling funds. I think there are probably more than 100 rolling funds out there, and probably 95% of them are [headed by] people who are working at the big tech or private tech companies, and it’s more of a vehicle of convenience for their friends to invest alongside them.
TC: And you think they need more capital than is floating out there already?
MK: I think we are the only institutional LP that is focused at this stage, because as you know, many of the funds of funds and university endowments and family offices have to write big checks, so they’re not going to be investing a little bit into a tiny $10 million fund.
TC: What are you looking for exactly?
MK: The goal is to find the next Lowercase Capital. Not everyone knows this, but Chris Sacca’s first fund was $8 million and it returned 250x. Manu Kumar of K9 Ventures — his first fund was $6.25 million and returned 53x. So you can generate substantial alpha with these smaller funds.
Historically, we would meet with fund managers, and when they said, ‘We’re going to raise a $10 million to $15 million fund,’ we were like,’Okay, sounds interesting. Let’s talk when you’re raising your second fund.’ But we realized that we’re missing out an entire segment of the market. So Nano was created to capture that.
TC: Why draw a line in the sand at $15 million?
MK: First, if you’re going to be running a $100 million seed fund, you have to be writing $1.5 million to $2 million checks, and that’s a super competitive space right now, because not only are there other seed funds but also a lot of firms — Founders Fund, Sequoia Capital, Lightspeed, General Catalyst — that are very active at the seed stage. We’re coming across a lot of these managers who want to stay small, because by writing $300,000 to $400,000, they’re not competing against Sequoia or Forerunner Ventures; they’re just sliding into the round.
TC: Do you worry they will just get washed out of that investment later through subsequent checks from bigger players?
MK: Right now, we now have more than 100 portfolio funds within Cendana, and we did some data analysis. We looked at the fund size, and then the average ownership of each fund. And it turns out there’s a baseline of about 15% of a fund, meaning if you’re a $100 million fund, the average ownership stake [you have in your startups] is around 15%. If you’re a $50 million fund, the average ownership is about 7.5%.
We then looked at performance across our fund managers, and it turns out that of funds with $50 million in capital — our better-performing funds — have more ownership than 7.5%. They have more like 10% to 12%. Now, when you look at these tiny funds, if you’re a $15 million fund, 15% of that [should equate to] 2.2% ownership, but we are seeing that these tiny funds are actually getting more like 4% to 5% ownership. They’re punching above their weight because of who is involved.
TC: Who have you backed so far?
MK: The first one is Form Capital, a fund from Bobby Goodlatte and Josh Williams. Both were early at Facebook; Bobby led the team that designed Facebook Photos and was later an [entrepreneur-in-residence] at Greylock. Josh cofounded Gowalla (acquired by Facebook).
TC: How big a fund are they raising and how much are you giving them?
MK: They raised a $15 million fund, and our strategy is to [account for] 20% of [each of these funds], so we wrote them a $3 million check.
The second fund manager is Jeff Morris Jr.; he runs a fund called Chapter One. He was a senior product guy at Tinder and and an active angel, and he raised a $10 million fund last year into which we wrote a $2 million check.
TC: And the third?
MK: The third manager hasn’t closed the fund, so I can’t disclose his name, but he was a very early employee at Uber and ran their data teams.
The last is an interesting example because this person could probably go out and raise $100 million, but to my point about not wanting to compete against everyone in the world in writing a big check, he’s content to write [sub $500,000] checks into interesting data analytics and AI and machine learning companies, and everybody wants him involved because of his experience and his network of data scientists worldwide.
TC: When Chris Sacca dove in, it was his full-time job, I think. Do you care if these managers are focused solely on investing?
MK: No. With Nano we’re investing in people who may actually have a day job, which would not be a fit for our main fund, but with our Nano fund, our aperture is wider. We welcome anyone out there looking to manage $15 million or less to reach out.
TC: Well, to be clear, you have some criteria. What is it?
MK: No matter who we invest in, they have to have investment experience and an investment track record. What we really look for at the end of the day is a person who has some sort of advantage — whether it’s domain expertise or networks. So you could be an amazing computer scientist in Pittsburgh at Carnegie Mellon and if you’ve made some investments [we’d talk with you]. It could be someone coming out of Stripe or PayPal or Facebook or an entrepreneur in Atlanta.
TC: A $30 million fund of funds is going to get committed pretty fast in this market. Is the plan to raise maybe one every year?
MK: We have an incredible top of the funnel, and as you’re alluding, we’re going to be inundated. But we walk in there and try to meet with everybody.
We’re also in discussions with our existing fund managers to create a nano fund for [some of] them. So, you know, imagine one of our fund managers, running a $100 million fund. Why not create a $10 million nano vehicle with them where they could write $250,000 to $500,00 check? They don’t want to fill up their fund with these small checks, but you could see how, if they were to create this smaller vehicle, it could be very interesting for them for a returns perspective.
TC: So you’d write them a check for a third of this nano fund . .
MK: And their LPs would fill in the rest. I’m sure they’d be excited to do it.
via Tingle Tech